According to the non-profit Solar Energy Industries Association, there are over 121 GW of solar capacity established in the United States today. That’s enough energy to power 23.3 million homes.
Yet, that doesn’t mean there are actually 23.3 million homes currently powered by solar energy. Instead, most solar panel systems today are “net-metered.” They’re connected to the power grid.
Solar batteries offer an intriguing alternative to conventional net metering.
Typically, when a home with solar panels uses less energy than what its panels generate, it exports the extra energy back to the grid. When a home uses more energy than its solar panels currently generate, it pulls from the grid to compensate. Net metering lets utility companies reimburse homeowners for the excess energy with utility bill credits.
Solar batteries give homeowners another option. Instead of exporting excess energy to the grid, the solar panel system can store the energy in a battery. Then, the home draws from the stored energy, rather than the grid, when the panels aren’t producing energy.
This is useful, but it also has some drawbacks. Read on to discover exactly how solar batteries work, existing solar battery options, and how to decide if batteries are right for you.
What Are Solar Batteries, Exactly?
Most solar power systems use photovoltaic panels and concentrated solar power devices. These technologies transform sunlight and heat into electrical energy.
Solar batteries receive and store this energy chemically. The unique chemical compositions of different battery types enable them to hold energy at a molecular level. To use the stored energy, the system triggers a chemical reaction that breaks chemical bonds.
This release is called “discharge.” A solar battery’s depth of discharge tells you how much of the stored energy it can functionally release without accruing damage.
Are Solar Batteries Worth It?
Consider the pros and cons of solar batteries before you invest in one. The up-front costs can be steep, and their value varies depending on your energy use and maintenance needs. Yet, for many, solar batteries prove to be a lifesaving asset.
Benefits
The benefits of solar batters can be summed up as “savings.” They save you money, time, and stress—in the right circumstances. Of course, the greatest benefit is how they help save the planet by reducing your carbon footprint.
1. Emergency Power During Blackouts
During a power outage, buildings cannot draw energy from the grid. But, a solar battery will still be functional. As the power grid ages, having backup power ready comes in handy more often.
2. Slash Your Energy Bills
Homes only draw energy from the grid if their batteries run out of power. This cuts their electric bills. Homeowners only pay for the difference.
3. Eliminate “Energy Tariff” Costs
Some electric companies charge “time of use” tariffs. These are surcharges imposed for using energy at certain times. With solar batteries, homeowners can dodge those costs by drawing on stored power during those windows.
Drawbacks
Drawbacks vary depending on what type of solar battery you install. That said, some drawbacks—like increased maintenance—are true across the board.
1. Higher Up-Front Costs
Solar energy storage increases the upfront cost of your solar power system. Batteries can cost anywhere from $5000-$14,000. Installation costs typically run $800-$2000. These costs are stacked on top of the cost of the solar power system itself.
2. Increased Maintenence Required
Batteries increase the complexity of your system. This, in turn, increases the risks of failure. With some batteries, you must regularly maintain cables, terminals, and ventilation. That said, LI-ON and saltwater batteries require less maintenance than others.
3. Battery Life vs. Solar Power System Life Mismatch
Typical solar batteries don’t last as long as the system as a whole. You’ll likely have to replace your battery at least once in your system’s lifetime.
How to Choose a Solar Battery
Which battery features are the most important to you? Most homeowners weigh the relative value of the following six metrics before investing:
- Power rating
- Capacity
- Lifespan
- Roundtrip efficiency
- Safety
- Cost
Costs are typically incurred up-front. These might include the cost of materials, installation, and replacement. As developers invest in certain technologies, costs tend to go down over time.
Best Solar Battery Models, Technologies
Since the 1980s, engineers have developed and improved upon energy storage technologies. Six solar battery models are either widely used today, or likely to surge in popularity in the near future. These models include:
- Nickel Cadmium (Ni-Cd)
- Lead Acid
- Flow
- Redox
- Hybrid
- Membraneless
- Organic
- Lithium-Ion
- Saltwater (Sodium-Ion)
- Hydrogen Fuel Cell
Of these six, the most popular on the market today are lead-acid, lithium-ion, sodium ion, and flow.
Environmentalists are trying to phase out Ni-Cd batteries due to cadmium’s toxicity. But, they’re pretty durable. Hydrogen fuel cells have a lot of potential, but most are not yet market-ready.
Lead Acid
Lead-acid batteries are the least expensive. Solar power systems have utilized them the longest. But, they’re also the most high-maintenance, as they require articular ventilation to function safely.
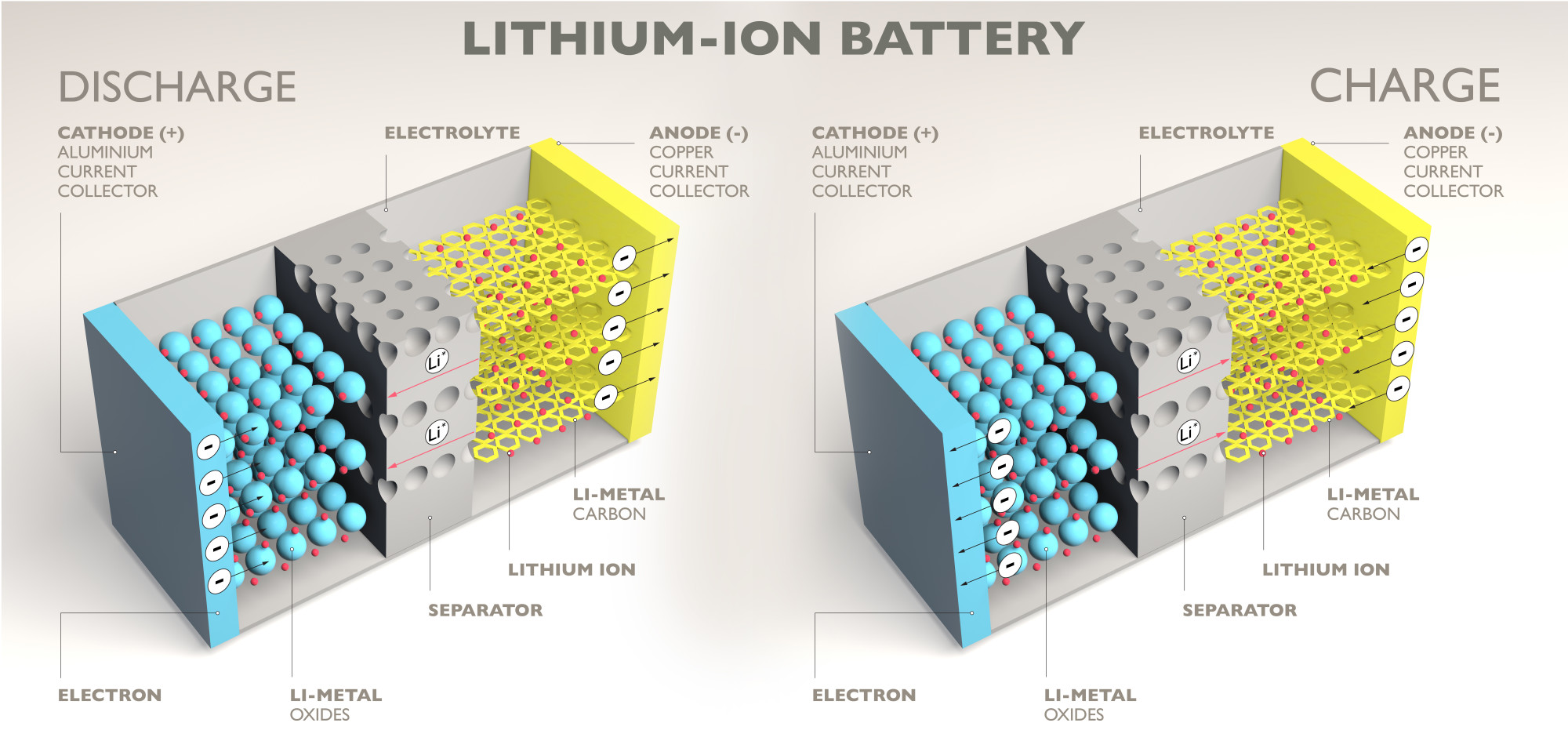
Lithium-Ion
Lithium-ion batteries are the most popular. They have a relatively high storage volume and energy density, a longer lifespan than lead-acid batteries, and a lower price point than most alternatives. But, these batteries are not the absolute cheapest option.
And, LI-ON batteries run the risk of accidental fires caused by thermal runaway.
Saltwater (Sodium-Ion)
Saltwater batteries are the most ecologically friendly; creating and recycling them doesn’t harm the environment. They also have the longest lifespan of all the batteries listed here.
Unfortunately, sodium-ion batteries have a lower energy density. This makes them bulkier, which raises production costs.
Flow
Flow batteries use two or more chambers of electrochemical fluid.
The fluids store energy via ion exchanges. They may or may not be separated by a membrane. Engineers exploit the properties of the fluids, which then enables virtually unlimited energy storage.
Flow batteries are the safest, as they’re both non-toxic and flame-retardent. But, they’re also the most expensive option.
Currently, scientists are researching better flow battery designs and electrochemical composition. These include zinc sediment slurry, hydrogen-bromide, and nitroxide compounds.
Discover Solar Power Companies Near You
Solar power is a pillar of the future of energy. Start moving forward with a solar panel system of your own. Whether you’re interested in net-metered savings, backup solar batteries, or going off-grid entirely, there’s a system that’s right for you.
Explore our directory to find a solar power provider in your state. Or, contact us online for a free estimate of how much you could save with solar power.